Neurons may need to send signals rapidly over long distances. The anatomical specialization that allows A Schematic Introduction to the Membrane Potential and Voltage Gated Channels During the Action Figure 3: The change in potential during an action potential, with its components labeled.Study Chapter 48: Neurons flashcards. Play games, take quizzes, print and more with Easy Notecards. 28) After the depolarization phase of an action potential, the resting potential is restored D) Movement of ions during the action potential occurs mostly through the sodium pump.Action potentials are the rapid changes in charge across the membrane that occur when a neuron is firing. Action potentials occur in three main stages: depolarization, repolarization and a refractory period.the initiation of the action potentials would be blocked. The KCl treatment could in itself also depolarize the postsynaptic terminal and that could lead to calcium entry. TTX is a sodium channel blocker and in neurons it blocks the production of action potentials, and thus its propagation too.There are a few components to the action potential. On a graph, plotting membrane potential vs. time, the slope become steep and the potential goes over 0 mV in the overshoot phase. After it comes back down, the potential undershoots, and the resting potential returns.
Chapter 48: Neurons Flashcards | Easy Notecards
There are many steps detailing the depolarization and repolarization of axon nodes to describe how an action potential is transmitted from a neuron. But, after looking at many different sources, I still see one clear thing missing: what causes the action potential in the first place? Every source simply says...During an action potential a rapid depolarization occurs that actually causes a reversal in the There are three distinct phases in an action potential that depends upon the electrochemical Either the depolarization does not reach threshold and triggers no action potential or it reaches threshold...During this period of hyperpolarization, another action potential cannot be triggered. Synthetic and natural molecules may affect different phases of the action potential, and thereby, affect the This results in a prolonged state of depolarization. Local anesthetics such as Novocain and Xylocaine...Action potentials are triggered when enough depolarization accumulates to bring the membrane potential up to threshold. When an action potential is triggered, the membrane potential abruptly shoots upward, often reaching as high as +100 mV, then equally abruptly shoots back downward...

An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of...
In a neuron, during the depolarization phase that may trigger an action potential _____. - most voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels are open - most voltage-gated sodium channels become inactivated - most voltage-gated sodium channels are open - some...(USMLE topics) What is Action Potential? How is it Generated in Neuron? Clear and Concise Explanation of Phases. This video is available for instant...An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane Neurones communicate with each other via brief electrical signals known as action potentials. They are brief changes in the voltage across the...During action potential triggered by a stimulus, a number of events take place in the neuron. These include: Depolarization - When a signal In a normal nerve cell, these structures are present and enhance the propagation of action potential. The areas covered with the myelin sheath prevent the...Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know. Whether it's to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; people...
There are several possible answers, which is partly why the assets you're reading are being imprecise: they are discussing the chain of occasions that happen after the initial depolarization, the source of which doesn't matter much for that chain of occasions.
Receptor potentials
Sensory receptors consist of some equipment that ultimately result in ion channels opening, frequently cation channels. This machinery can also be direct, the place a stimulus without delay opens an ion channel, or it might probably me mediated through g-protein coupled receptors. There are many many examples, but one favorite toy instance is the TRPV1 receptor, a part of the "transient receptor potential" family.
TRPV1 channels open when uncovered to prime temperatures or chemical agonists like capsaicin (which supplies chili peppers their 'heat').
There are automatically gated channels in the inside ear that are stretched open as sound waves move; there are G-protein coupled receptors in the retina that are activated in response to gentle - when they are activated, they shut channels which reduces neurotransmitter free up and therefore adjustments the amplitude of the post-synaptic polarization.
Ligand-gated ion channels
Synaptic transmission between neurons is regularly mediated via ion channels that are gated by neurotransmitters. A presynaptic cellular releases a neurotransmitter, for instance glutamate, and that neurotransmitter binds glutamate receptors on the post-synaptic mobile, for example AMPA receptors. These receptors are non-specific cation channels, and when they open sodium comes in and depolarizes the mobile. Other neurotransmitters, together with inhibitory ones, paintings a similar means.
Gap junctions/eletrical synapses
Although they just happen between specific populations of neurons in mammalian fearful programs (for instance, some inhibitory networks in the mind and between cardiac myocytes), some cells are coupled via channels that allow ions to cross between cells. Therefore, depolarization in one cellular may also be transmitted by means of ions flowing thru that gap junction and begin to depolarize the adjacent cell.
Intrinsic conductances
It does not actually follow in the context of a "stimulus" however in some types of cellular there are intrinsic conductances that can convey a cellular to threshold and trigger an action potential. One instance can be in the pacemaker cells of the sinoatrial node that start up cardiac contractions.
chapter 12 practice questions Flashcards | Quizlet
Mechanisms and structures involved in the pathogenesis of ...

Instrumentation: Understand Sod ium pump and transmission ...

2 shows the basic steps of an action potential, where the ...

Normal value of sodium and potassium. What causes high ...

The membrane action potential of pacemaker cells and the ...

Activation and Reconfiguration of Fictive Feeding by the ...

(PDF) Molecular Physiology of Low-Voltage-Activated T-type ...

Exam 2 - Neuroscience 109 with Strand at Oakland City ...

Activation and Reconfiguration of Fictive Feeding by the ...

Mechanisms and structures involved in the pathogenesis ...

Image showing what happens when action potential arrives ...

What is the difference between action potential and ...

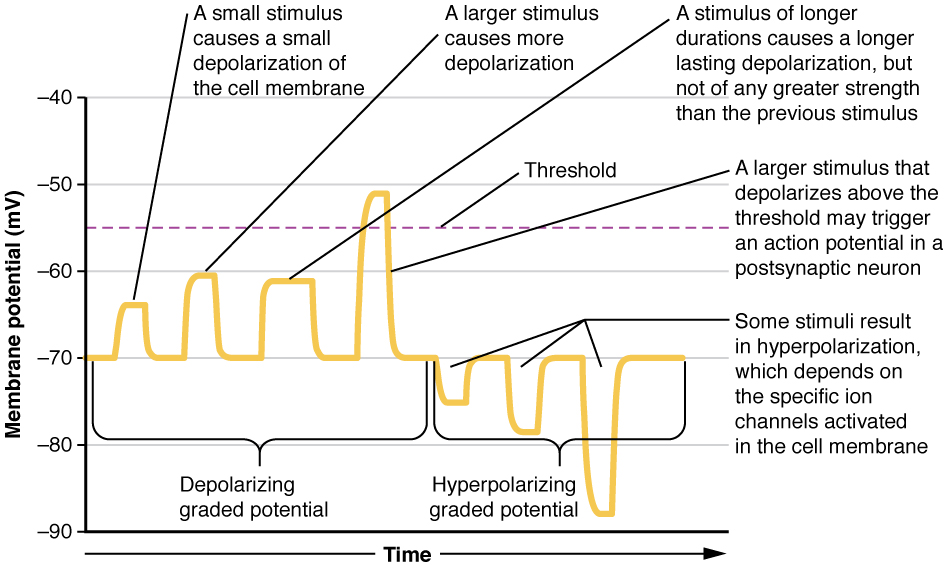
Graded potential - Wikipedia

Action potential (niraj)

Graded potential - Wikipedia
2: Heart potential diagram A typical action potential wave ...

Process of Hyper-polarization to baseline in neuron AP ...

Action potential graded potential. neuroscience. 2019-01-06
assignt.htm

Refractory period (physiology) - Wikipedia







No comments:
Post a Comment